The 3 ACCESSORY ORGANS of the digestive tract (pancreas, liver and gallbladder) facilitate digestion and absorption in the small intestine.
The Pancreas
Pancreas contains endocrine and exocrine cells
- Endocrine cells contained in tail, islet cells of Langerhans
- A cells - glucagon
- B cells - insulin
- D cells - somatostatin
- Exocrine cells contain acinar secretory cells arranged in a circular pattern around small ducts
- Duct cells produce alkaline rich juice
- Acinar cells produced granules of digestive enzymes that get released by exocytosis into the lumen of duct cells
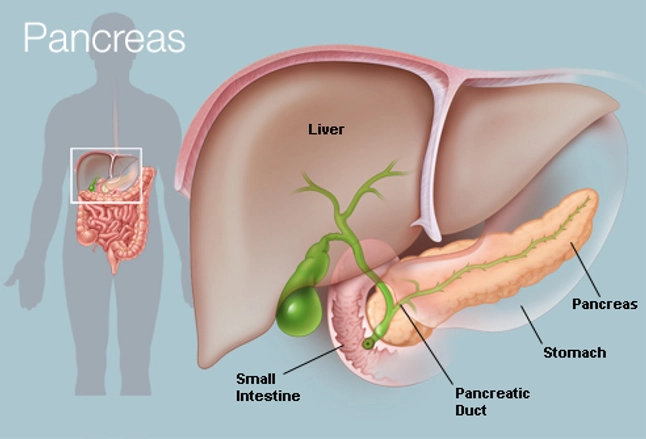
- Ducts coalesce to form the pancreatic duct of Wirsung which runs the length of the panreas and connects to the common bile duct at the ampulla of Vater to form the common channel (bile pancreatic duct) which empties through the sphincter of Oddi
- Produces 2L daily
- Juice contains:
- Water
- Electrolytes:
- Cations: Na, K, Ca
- Anion: Cl
- Bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
- Acinar Cells release enzymes and digest 50% carbs, 50% protein, 80-90% fats
- Proteases - enzymes that digest proteins are released inactive as Zymogens (otherwise would digest pancreas)
- Zymogens: trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidases, proelastase, collagenase
- Zymogen trypsinogen is important as it activates others
- Trypsin inhibitor is present in the pancreas to ensure that activation does not occur in pancreas
- Hydrolyze peptide bonds within protein
- Pancreatic alpha-amylase digests starch
- Fat digestion
- Enzymes: lipase, phopholipase A2, colipase
Regulation of Pancreatic Secretions
- Primary stimuli for release of pancreatic juice:
- Secretin released when unneutralized acid chyme in duodeunum
- CCK released in response to fat and protein
- Pancreatitis
- Cause: etoh, hypertriglyceridemia (TG > 1000 mg/dL), pancreatic duct obstruction, viral infection, inury
- Dx: amylase and lipase in serum
- RX: partially hydrolyzed food, supplement with lipase
The Liver
Bile Synthesis and Function
- Bile: a detergent that emulsifies fat to micelles that allow lipase to digest fully.
- bile acids
- synthesized in hepatocytes from cholesterol which is oxidized to generate CHENODEOXYCHOLIC ACID and CHOLIC ACID
- salt
- bile acids combine with Na > K or Ca then conjugate with amino acids glycine or taurine
- Lecithin - made of cholesterol & phospholids
- bile pigment - waste of Hg degradation, conjugated in liver with glucuronic acid
- Bilirubin
- Biliverdin
- dissolved in alkaline solution - water and bicarbonate
The Gall Bladder
The Recirculatioin and Excretion of Bile = ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION



No comments:
Post a Comment